Understanding Overload Protection in Power Strips
Overload protection1 is one of the most essential features in any power strip, helping prevent overheating, fire, and damage to connected devices.
Overload protection1 in power strips works by automatically cutting power when the total connected load exceeds the rated capacity. This safety mechanism helps avoid electrical fires, equipment failure, and costly downtimes in both residential and industrial environments.
Let’s dive into how it works, why it matters, and how to keep it functioning optimally.
What Is Overload Protection and How Does It Work in Power Strips?

Overload protection1 prevents a power strip from drawing more electrical current than it’s rated to handle.
When the combined power demand of connected devices exceeds the strip’s maximum current rating (measured in amps or watts), an internal circuit breaker or thermal fuse is triggered. This automatically shuts off the power flow to prevent overheating and fire.
Power strips without overload protection may continue supplying current until internal components melt or wiring insulation fails—posing serious risks.
Key Components of Power Strip Overload Protection Systems
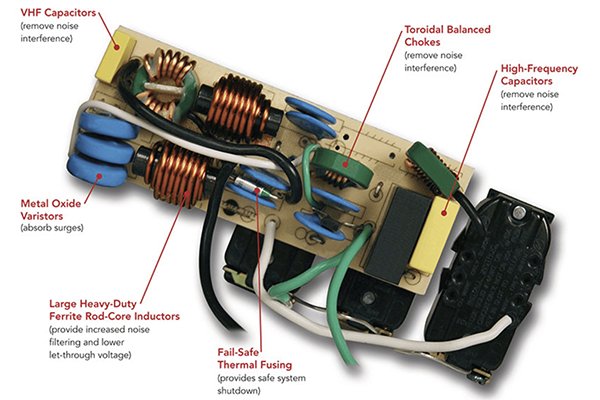
A power strip’s overload protection system typically includes:
- Circuit Breaker Switch2 – A resettable device that trips when excessive current is detected.
- Thermal Fuse3 – A one-time fuse that cuts off power when the internal temperature reaches unsafe levels.
- Surge Suppression Circuit4 (if included) – While not the same as overload protection, this works alongside it to manage voltage spikes.
- Indicator Lights – These show whether protection is active or if a reset is needed.
These components work together to sense, interrupt, and signal abnormal power conditions.
Benefits of Choosing a Power Strip with Overload Protection

Investing in a power strip with built-in overload protection brings several key advantages:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Fire Prevention5 | Stops overheating and fire caused by electrical overloads |
| Device Safety | Protects computers, appliances, and tools from damage |
| Compliance | Meets UL, CE, or ETL safety standards6 |
| Peace of Mind | Reduces risks during unsupervised use or in shared environments |
For buyers in regulated markets like the U.S. and EU, overload protection is often mandatory to pass safety inspections.
How to Test and Maintain Overload Protection for Long-Term Safety

Proper use and maintenance ensure your power strip’s protection mechanisms stay reliable:
- ✅ Test the reset button monthly if your model has one.
- 🚫 Avoid daisy-chaining multiple power strips, which can bypass protection.
- ⚠️ Check device wattages before connecting. Do not exceed the strip’s total capacity.
- 🔍 Inspect regularly for cracks, burn marks, or melted plastic.
- 🔁 Replace immediately if the power strip fails to cut off during obvious overload situations.
Tip: A safe rule of thumb is to keep total load under 80% of the strip’s rated capacity.
✅ Conclusion
Overload protection1 is not just a nice-to-have—it’s a critical safety feature that safeguards people, property, and equipment. When selecting a power strip, always prioritize certified models with built-in overload protection, and maintain them regularly to ensure they work when it matters most.
-
Understanding overload protection is crucial for safety and device longevity. Explore this link to learn more about its importance. ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩
-
Discover how circuit breaker switches enhance safety in power strips, preventing electrical hazards and ensuring device protection. ↩
-
Learn about thermal fuses and their role in preventing overheating, a key aspect of power strip safety. ↩
-
Explore the function of surge suppression circuits and how they protect your devices from voltage spikes. ↩
-
Understanding fire prevention features in power strips can help you choose safer options for your home or office. ↩
-
Familiarize yourself with safety standards to ensure your power strip meets necessary safety requirements. ↩






