Top 5 Quality Tests Every Power Strip Must Pass

If a power strip is going to live under a desk for years—feeding a hungry PC, a big monitor, and a tangle of chargers—it must prove it’s safe, durable, and compliant. Here are the five test pillars I insist on before any unit ships.
1. Electrical Safety Test1: Overload and Short-Circuit Protection

What we test
- Overload trip & reset2: Verify the resettable breaker (or thermal cut-out) trips at the rated current (e.g., EU 10A/13A, US 15A) and resets cleanly after cooling.
- Short-circuit tolerance: Confirm the protection clears faults without flaming or cracking; enclosure must contain the event.
- Earthing/ground continuity: Measure resistance from earth pin to every earthed contact (typically ≤0.1–0.2 Ω).
- Leakage current: Ensure touch-safe leakage under normal and single-fault conditions.
Why it matters
- Prevents silent overheating (the cause of too many fires).
- Guarantees a predictable, safe failure mode when something goes wrong.
Good signs
- Crisp trip at spec, cool-down reset within minutes, and no scorching on the PCB or contacts.
2. Surge Protection and Voltage Withstand Test3
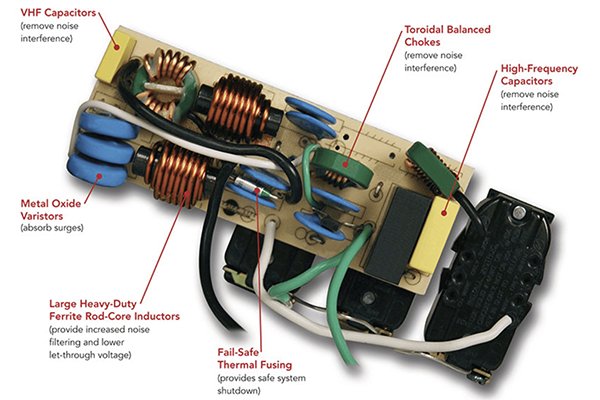
What we test
- Surge endurance4 (if surge-protected model): Combination-wave hits (e.g., 1.2/50 µs – 8/20 µs) at defined kV/A to validate the joule rating and MOV + thermal disconnect behaviour.
- Clamping performance: Check let-through voltage stays within design; indicator LED shows when protection is spent.
- Dielectric strength5 (hi-pot): Apply high AC voltage (often 1,500–3,000 Vac depending on standard) between live parts and accessible metal to prove insulation integrity.
Why it matters
- Real mains have spikes—from storms to switching loads. Proper surge stages keep noise and transients away from your gear and fail safe when exhausted.
Good signs
- MOVs are thermally fused; no catastrophic venting; clamping remains consistent across pulses; protection LED logic is honest.
3. Durability and Heat Resistance Test6
What we test
- Temperature rise at rated load: Continuous run at 100% load; measure hotspots at terminals, traces, plug pins, and cord entry.
- Glow-wire / ball-pressure / flame rating: Plastics meet UL94 V-07 (or equivalent); glow-wire tests ensure self-extinguish behaviour.
- Mechanical endurance:
- Socket insertion/withdrawal cycles (thousands of mates)
- Switch life (≥10,000 toggles)
- Cord flex at the strain relief (figure-8 bend test)
- Contact wear & retention: Plug blades must hold firmly without excess heat from poor contact pressure.
Why it matters
- Heat is the silent killer. If plastics soften or contacts loosen, resistance rises—and so does fire risk.
Good signs
- Temperature rise stays within spec; no deformation; socket grip remains firm after endurance cycles.
4. Certification and Compliance Test8: CE, UL, ETL, and RoHS

What we verify
- Market safety files:
- EU/UK: CE/UKCA with harmonised standards (e.g., EN 62368-1/60335 where applicable, EN 61643 for surge, EN 55032/35 for EMC).
- US/CA: UL/ETL listing to relevant clauses (including abnormal operation, strain relief, temperature, dielectric).
- EMC & radio (smart strips): FCC (US) and RED (EU) for emissions/immunity and wireless.
- Materials: RoHS (hazardous substances) / REACH (SVHC) declarations.
- Labelling & documents: Proper ratings, symbols, country-specific warnings, DoC (Declaration of Conformity), and traceable serial/QR codes.
Why it matters
- Compliance isn’t a sticker—it’s a repeatable process that prevents customs delays and protects users.
Good signs
- Test reports issued within the last 24 months, production audit records, and artwork/label files that match what’s in the box.
5. End-of-Line Functional & Inspection Tests9 (Every Unit)

What we do on 100% of units
- Hi-pot and ground continuity checks at the end of the line.
- Polarity & wiring verification (L-N-E) and switch illumination/LED status.
- USB-C/USB-A power map10 verification (if present): per-port voltage/current and shared budget under load.
- Visual QC: Solder quality, correct MOV & fuse link placement, torque on terminal screws, smooth action on the reset switch.
Why it matters
- Type tests prove the design; end-of-line tests protect your brand unit by unit.
Sample Test Plan (cheat-sheet)
| Area | Test | Typical Target |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical safety | Overload trip/reset | Trips at rated current; auto reset after cool |
| Insulation | Hi-pot | 1.5–3.0 kVac pass, no breakdown |
| Ground path | Continuity | ≤0.1–0.2 Ω |
| Surge (SPD models) | Combination wave | Clamps within spec; safe end-of-life |
| Thermal | Temp rise @ 100% load | Below standard limits; no softening |
| Materials | Flame & glow-wire | UL94 V-07; self-extinguish |
| Endurance | Socket & switch cycles | Meets/Exceeds cycle count |
| Compliance | CE/UKCA / UL/ETL / RoHS | Valid reports + DoC/labels |
| EOL | Polarity, LEDs, USB power map | 100% verification |
Conclusion
Any power strip worth buying (or selling) proves five things: it trips safely, shrugs off surges, runs cool for years, carries real certifications, and every single unit leaves the line electrically sound. If even one of those pillars is missing—walk away. Your customers, and their gear, are counting on it.
-
Understanding this test is crucial for ensuring the safety and reliability of power strips. ↩
-
This feature is essential for preventing overheating and ensuring user safety. ↩
-
This test is vital for protecting your devices from electrical surges and ensuring longevity. ↩
-
Understanding surge endurance helps in choosing power strips that protect against electrical spikes. ↩
-
This property is crucial for ensuring insulation integrity and preventing electrical failures. ↩
-
Learn about this test to understand how power strips can withstand heat and wear over time. ↩
-
This rating indicates the fire safety of materials used in power strips, ensuring user safety. ↩ ↩
-
Certifications ensure that power strips meet safety standards, protecting users and devices. ↩
-
These tests guarantee that every unit meets quality standards before reaching consumers. ↩
-
This feature is important for understanding power distribution across multiple devices. ↩






