We see more and more eco-friendly packaging on shelves these days. But how exactly does Europe handle recyclable packaging, and what rules help keep it all on track?
The European Union has introduced stringent packaging regulations aimed at reducing waste, improving recyclability, and promoting a circular economy. From setting minimum recycled content requirements to encouraging reusable packaging, these regulations inspire both manufacturers and consumers to adopt greener practices. This helps protect the environment while meeting rising consumer demands for sustainability.
It’s exciting to see these changes unfold.
What are the new EU rules for packaging?
Most European packaging rules revolve around minimizing waste and ensuring that materials can be easily recycled or reused.
Under the latest EU directives, packaging designers must reduce unnecessary materials, increase recycled content in their products, and label packaging clearly to inform consumers about proper recycling. These rules target reductions in single-use plastics, encourage compostable materials when feasible, and demand that all packaging placed on the market is either reusable or recyclable by 2030. This ambitious plan pushes businesses across Europe to rethink their packaging strategies and invest in innovative technologies, ensuring long-term environmental benefits and helping the EU move closer to its circular economy goals.

Dive deeper into the new rules for packaging (At least 200 words, with H3 headings, no conclusion here; add line breaks for readability; try to add md format tables):
At Howdy, I’ve noticed that customers in Germany and France often ask if our packaging meets European sustainability standards. Their concerns match the growing emphasis on eco-friendly materials, a shift seen across the EU. Below is a look at key aspects of these new rules:
1. Reducing Overpackaging
One of the main targets is to prevent unnecessary material use—no more boxes twice the size they need to be. This approach cuts costs for businesses and limits waste generation.
2. Mandatory Recycled Content
The EU mandates minimum thresholds for recycled materials in packaging. For instance, plastic packaging1 must incorporate a certain percentage of post-consumer recycled (PCR) content. By implementing these standards, it encourages a robust market for recycled plastics.
| Material | Target Recycled Content (%) |
|---|---|
| Plastic | 30 |
| Paper/Cardboard | 85 |
| Metals | 50 |
3. Uniform Labeling
Clear, standardized labels help consumers sort packaging correctly. From color-coded bins to straightforward recycling icons2, simple instructions reduce contamination in recycling streams.
4. Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR)
Under EPR systems, producers bear financial and/or administrative responsibility for the end-life management of their packaging. This model prompts companies to rethink design choices, ensuring easier recycling and waste reduction.
5. Timelines and Penalties
Businesses must comply with these regulations by set deadlines. Non-compliance can lead to hefty fines, production delays, and reputational harm. For those of us exporting from China, aligning with these rules ensures a smoother path into Europe’s markets.
Ultimately, these EU packaging rules serve as guidelines for a greener future, pushing companies like ours to develop creative, planet-friendly packaging solutions without sacrificing quality or design.
What are the EU standards for recycling?
European standards for recycling focus on creating a seamless system where materials are easily recoverable.
These standards center on defining recyclable materials, setting quality benchmarks for collected waste, and employing consistent waste-sorting infrastructures. By harmonizing collection systems and labeling practices, the EU strives to bolster both consumer participation and industrial processing, all while ensuring efficiency and eco-friendliness across member states’ waste management frameworks.

Dive deeper into EU standards for recycling (At least 200 words, with H3 headings, no conclusion here; add line breaks for readability; try to add md format tables):
My first encounter with strict European recycling standards came when I visited a Spanish supermarket. I noticed that every product had clear, color-coded symbols for disposal. This clarity wasn’t just for show—it directly ties into the EU-wide recycling standards3.
1. Material Classification
The EU categorizes recyclable materials into specific groups like plastics, metals, paper, and glass. Each category follows standardized procedures for collection and processing. This classification system reduces confusion at both consumer and industrial levels.
2. Waste Stream Management
European directives encourage separate waste streams to avoid contamination. For instance, in Germany, Gelbe Sack or yellow bags exist for plastics, while paper gets its own bin. This separation at source simplifies subsequent sorting steps.
3. Harmonized Labeling
To unify recycling efforts, EU labels typically feature recognizable symbols (like the Möbius loop and numeric codes indicating the type of plastic or material). This consistent approach educates people on proper disposal.
| Symbol | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Möbius Loop | General recyclability | Common on paper packaging |
| PET1 | Polyethylene Terephthalate | Water bottles, microwavable trays |
| HDPE2 | High-Density Polyethylene | Milk jugs, shampoo bottles |
4. Quality Control
Recycled materials must meet certain purity thresholds. For instance, recycled plastic must not contain harmful chemicals that compromise safety—particularly relevant for food-grade packaging.
5. Eco-Design Principles
Beyond sorting and collecting, the EU pushes producers to adopt eco-design. This includes life-cycle assessments, reduced plastic content, and easily separable packaging components.
For anyone exporting products to Europe, adhering to these rules is vital. At Howdy, we align our packaging designs with these European recycling standards4, ensuring that packaging for items like cable reels or power strips can smoothly pass through European waste management systems.
—
What is the EU recycling target for plastic?
EU plastic recycling targets are set to curb pollution and preserve resources.
By 2025, the EU aims to recycle at least 50% of plastic packaging waste, increasing to 55% by 2030. These ambitious targets motivate companies to innovate in recyclable material sourcing, design for reuse, and more efficient waste collection methods. The overall goal is to reduce plastic pollution while promoting a circular plastic economy.
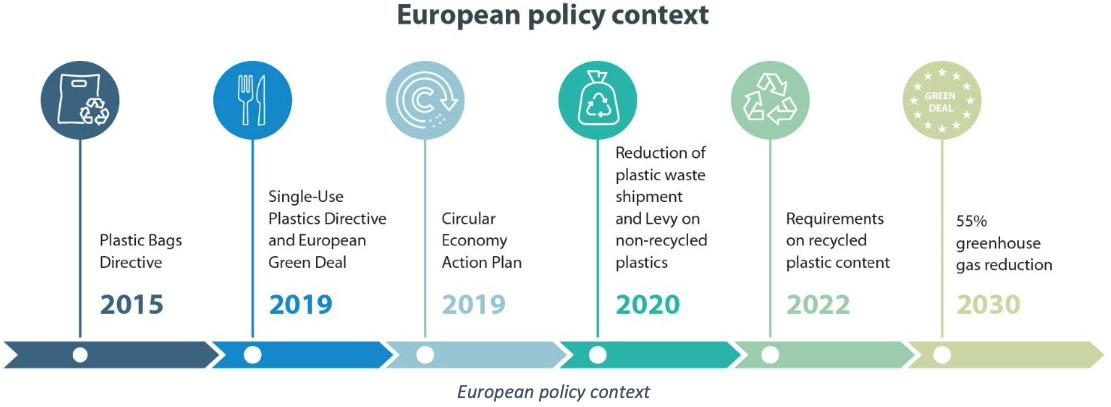
Dive deeper into the EU recycling target for plastic (At least 200 words, with H3 headings, no conclusion here; add line breaks for readability; try to add md format tables):
Seeing these targets in action reminded me of attending a trade fair in Paris, where eco-conscious buyers specifically asked if our plastics met EU plastic recycling thresholds5. These queries mirror a widespread consumer push toward truly green packaging—and the EU’s robust targets confirm this direction.
1. Timeline and Goals
The EU sets gradual milestones:
- By 2025: A 50% recycling rate for plastic packaging.
- By 2030: A 55% rate, with potential adjustments as technology advances.
2. Infrastructure Improvements
Achieving these targets requires investing in state-of-the-art recycling facilities. Member states are incentivized to expand collection points, upgrade sorting plants, and foster research into advanced recycling methods (e.g., chemical recycling for hard-to-recycle plastics).
3. Impact on Producers
Companies must adapt packaging designs to meet these recycling targets. For instance, producers may shift from multi-layer plastics to single-layer materials that are simpler to recycle. At Howdy, we’re also researching compostable film options where feasible, though we remain mindful of performance requirements for power strip packaging.
| Target Year | Recycling Goal for Plastic Packaging |
|---|---|
| 2025 | 50% |
| 2030 | 55% |
4. Consumer Engagement
Informing consumers about proper disposal significantly impacts plastic recycling rates. EU directives often require clear labeling, making it easier for individuals to place items in the correct bins.
5. Monitoring and Penalties
Member states must report progress to the European Commission. Failing to meet targets can result in penalties or mandated action plans. This fosters accountability and consistent effort across all states.
By proactively aligning with these plastic recycling goals6, businesses can build credibility and strengthen relationships with environmentally conscious customers, ultimately adding value beyond simple compliance.
What is the recycling rate for packaging in the EU?
The EU’s packaging recycling rates demonstrate impressive progress, yet there’s still room to grow.
Current reports reveal that over 60% of packaging waste in the EU is recycled, with some countries surpassing 70%. Despite this success, the EU aims to push these numbers even higher by introducing stricter regulations, encouraging research into innovative recycling solutions, and fostering cross-border collaborations.
Dive deeper into the recycling rate for packaging in the EU (At least 200 words, with H3 headings, no conclusion here; add line breaks for readability; try to add md format tables):
I recall scanning an official EU report 7showing that countries like Germany consistently rank among the top for recycling packaging. This high rate stems from a well-established waste management system and strong public engagement. But the EU’s broader goal is to ensure every member country matches—or even beats—these figures.
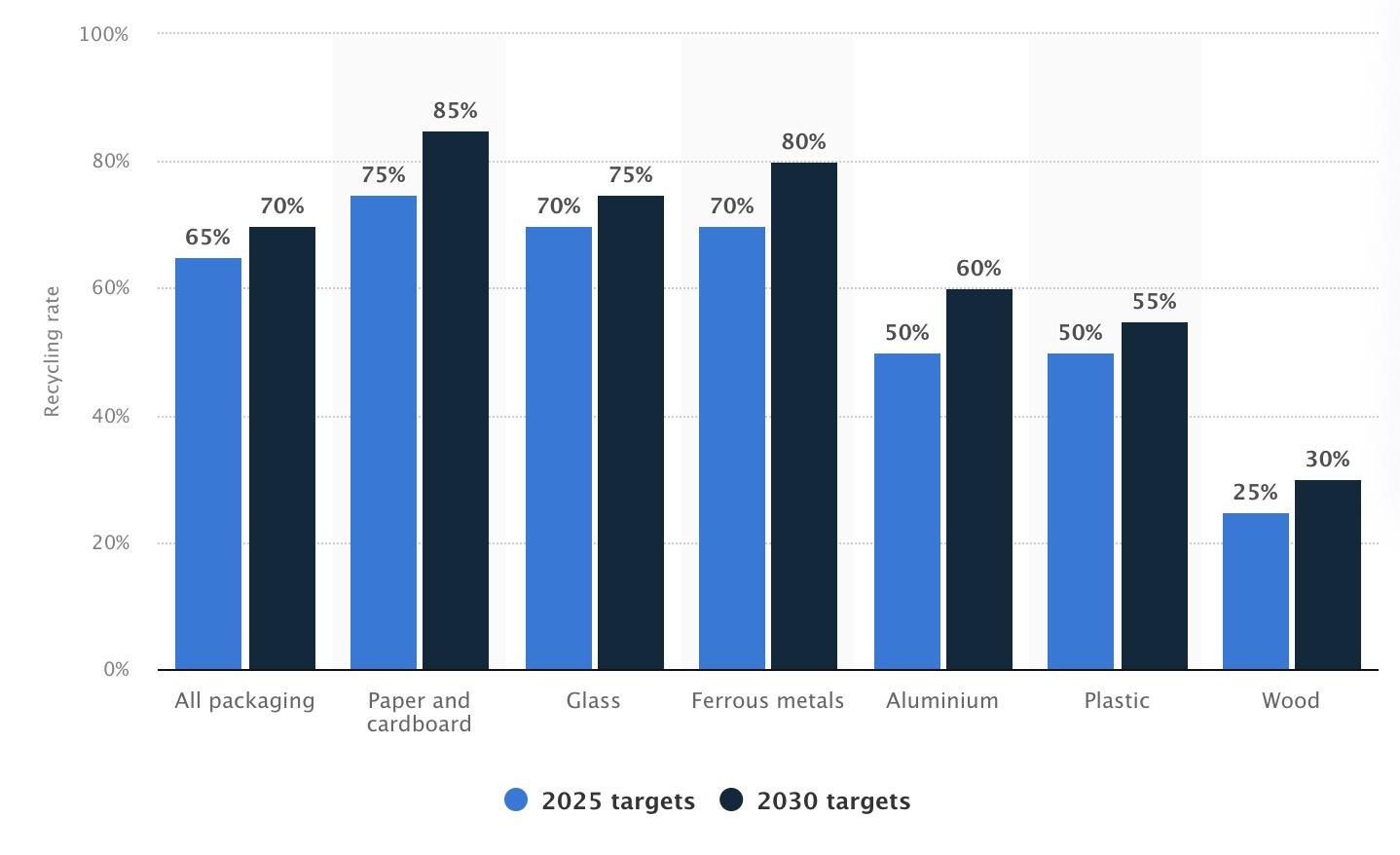
1. Statistical Snapshot
EU data indicates that packaging recycling averages around 66%. Material-wise:
- Paper and cardboard see the highest recycling rates, often exceeding 80%.
- Glass follows close behind, thanks to existing collection networks.
- Metals also maintain a decent rate, especially aluminum cans.
- Plastics lag somewhat, highlighting why the EU invests heavily in plastics recycling innovation8.
| Material | Approx. Recycling Rate (%) |
|---|---|
| Paper/Cardboard | 80+ |
| Glass | 75+ |
| Metals | ~70 |
| Plastics | ~40-45 |
2. Disparities Among Member States
Not all member states perform equally. Some countries have advanced infrastructures, high public awareness, and stringent waste policies, while others struggle with limited resources or inconsistent waste collection systems. Understanding these regional disparities is key to addressing the gaps.
3. Policy and Public Influence
The EU continues to refine directives to harmonize rates across regions. Public awareness campaigns, deposit-return schemes, and incentives for companies to invest in greener packaging all boost rates. In turn, this cultivates a recycling culture that resonates with local businesses and households.
4. Future Outlook
With continuous policy updates and technology breakthroughs, the EU aims to surpass 70% in the near term. By 2030, the aspiration is that every piece of packaging can be either reused or recycled, significantly reducing the region’s environmental footprint.
For a China-based supplier like Howdy, aligning with these ambitious targets involves designing packaging that easily enters the EU’s recycling stream—because a sustainable partnership builds trust and ensures long-lasting customer relationships.
Conclusion
Packaging rules in the EU evolve in tandem with rising sustainability expectations. From stricter regulations to ambitious recycling targets, these standards are reshaping how businesses handle packaging—from design right through to disposal. And for those of us at Howdy, it’s a chance to innovate, adapt, and create greener packaging solutions that resonate with eco-conscious markets.
-
Adding this link helps readers understand the specific obligations for plastic recycling, a major component of EU packaging reforms. ↩
-
This provides clarity about uniform labeling practices, empowering consumers to recycle effectively. ↩
-
This link helps readers understand the foundation of recycling guidelines across Europe, which are critical for compliance and sustainability. ↩
-
This link will help readers explore eco-friendly packaging practices encouraged by the EU for compliance and environmental benefits. ↩
-
This link helps readers understand the EU’s goals and how they impact the packaging industry. ↩
-
This link offers insights into strategies companies are using to align with EU policies, providing practical examples. ↩
-
This link helps readers access comprehensive data on the EU’s recycling rates, providing a factual foundation for informed discussions. ↩
-
Plastics recycling remains a challenging area, and linking to innovation efforts showcases the EU’s focus on tackling this issue. ↩







