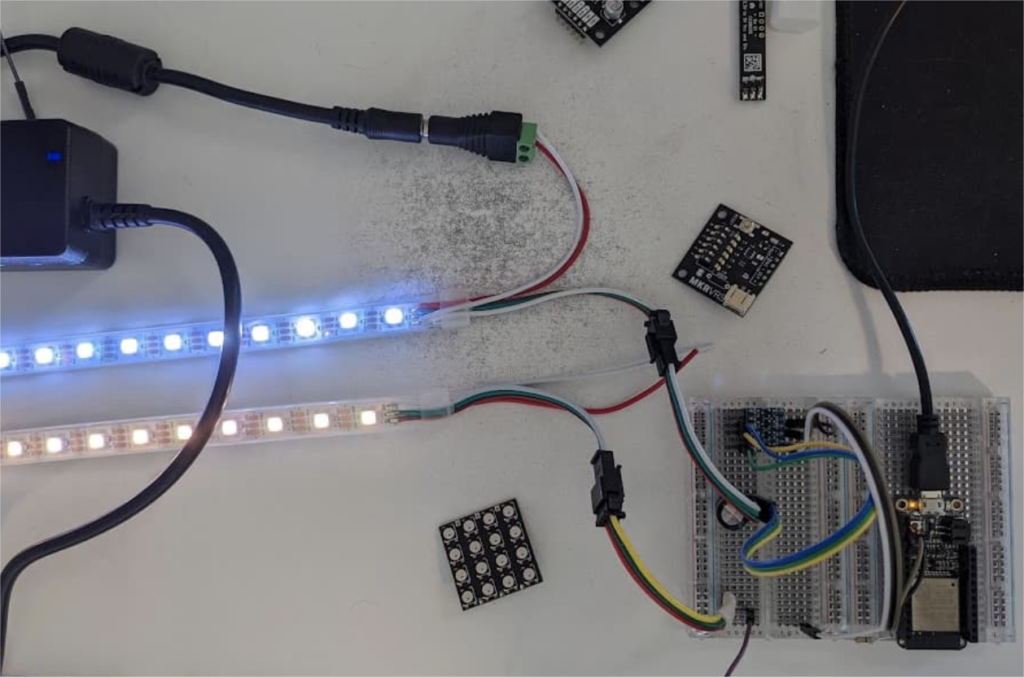
Can You Power an LED Strip with a LiPo Battery?
Yes, you can run an LED strip off a LiPo (lithium polymer) battery if you match the voltage and ensure proper current supply. LiPo packs offer lightweight portability and high discharge rates, but they demand careful handling. Let’s see how to do it safely and keep your LEDs shining bright.
Running a LiPo-powered LED strip is popular for portable lighting—like cosplay props, mood lighting, or small DIY projects. Just confirm your strip’s voltage (often 5V, 12V, or 24V) and choose a battery (or step-up/step-down regulator) that meets those specs. You’ll also need a LiPo-compatible charger and some basic safety practices. LiPos are more sensitive than alkaline packs—avoid overcharging or deep discharging. With a proper setup, you’ll enjoy bright, stable illumination on the go.
Let’s explore the essential voltage considerations, managing current capacity, safety tips, and best practices for extending battery life.
What Voltage Is Required for Your LED Strip?
LED strips commonly come in 5V, 12V, or 24V varieties. Matching these needs to your LiPo pack is crucial for stable brightness and circuit integrity.
Check your strip’s labeling or documentation. If it’s a 5V strip, you could run it directly off a single-cell LiPo (nominal 3.7V, up to 4.2V fully charged) but might need a boost converter for consistent 5V output. For 12V strips, either use a 3S (11.1V nominal) LiPo or incorporate a buck/boost regulator for precise voltage. A 24V strip typically requires multiple LiPo cells in series or a separate step-up module, making the setup more complex.

Voltage mismatch is the most common stumbling block. Single-cell LiPo packs range from 3.0V (near depletion) to 4.2V (fully charged). A 5V LED strip might run dim at lower voltages or flicker if the battery dips under 3.7V. To maintain stable brightness, a DC-DC boost converter can step up the LiPo voltage to 5V constantly, ensuring each LED receives enough power.
For 12V Strips
A single LiPo cell won’t suffice. You need three cells in series1 (3S), nominally 11.1V, with a full charge around 12.6V. However, as the pack discharges to about 9.0V total, your LEDs may dim. You can add a buck-boost regulator2 to keep a steady 12V output if uniform brightness is essential. Just be mindful that each regulator step costs some efficiency—your battery life might shorten slightly.
For 24V Strips
You might consider 6S LiPo setups (22.2V nominal, 25.2V fully charged) or a specialized step-up converter from a lower voltage pack. This is more advanced, so weigh simpler alternatives if your design allows.
Checking Voltage on the Fly
Because LiPo voltages vary throughout discharge, many hobbyists rely on a low-voltage alarm3 or battery monitor. This device alerts you when the pack is near depletion, preventing damage to the cells. Over-discharging LiPos significantly reduces lifespan and can pose safety risks.
By carefully matching your LED strip’s voltage needs, you’ll avoid flickering, dimming, or potential electrical damage. Whether you pick a single-cell with a boost converter or multiple cells in series, the key is ensuring consistent power for stable, vibrant light.
How Do You Ensure the Correct Current and Capacity?
An LED strip’s current draw depends on its length, brightness, and type of LEDs (e.g., 5050, 2835). Ensuring your LiPo can handle the needed amperes keeps your strip fully lit and the battery healthy.
Calculate total current by checking the strip’s wattage per meter or amps per section. Multiply by the length. If your strip draws 2 amps at 5V, you need a battery that can comfortably deliver 2 amps (or more) continuously. LiPos list capacity in mAh (milliamp-hours) and a C-rating indicating max discharge. For example, a 2200mAh pack at 10C can deliver up to 22 amps safely—well above 2 amps. But always keep some overhead to avoid stressing the pack or causing excessive heat.
LED strips are often rated in watts per meter. Let’s say you have a 5V strip using 14.4W per meter. That’s 14.4W ÷ 5V = 2.88A per meter. If you’re powering one meter, you’ll need a LiPo capable of delivering about 3 amps. For multiple meters, multiply accordingly.
Matching LiPo Capacity
A LiPo’s capacity (mAh) and C-rating define how much current it can output continuously. For instance:
- 2,200mAh 10C LiPo: 2.2Ah × 10 = 22A max safe discharge.
- 1,000mAh 20C LiPo: 1.0Ah × 20 = 20A max safe discharge.
You don’t need a huge discharge rating if your LED strip only draws a few amps. But having a bit of headroom helps the battery run cooler and last longer.
Considering Runtime
If your strip draws 2A at 5V, a 2,200mAh (2.2Ah) pack would theoretically run ~1 hour at full brightness (2.2Ah ÷ 2A = 1.1 hours). Real-world conditions and power converter inefficiencies shorten that estimate. If you need extended operation, pick a larger capacity or parallel multiple LiPo packs (though combining packs requires knowledge of LiPo balancing4).
Voltage Regulators Impact
Using a buck/boost converter5 also affects total current draw from the battery side. If you’re boosting voltage from 3.7V to 5V, the battery’s discharge current can be higher than the strip’s 5V current draw. For example, 5V at 2A is 10W. Boosting from ~3.7V means you might pull ~2.7A from the battery side to maintain 10W output (plus inefficiency). Ensuring your pack and converter can handle this is crucial.
By calculating both your strip’s current needs and the battery’s discharge capabilities, you’ll avoid underpowered or overheating setups.
What Safety Precautions Should You Take?
Lithium polymer batteries offer high energy density but require careful handling to prevent fires or explosions. Let’s see how to use them safely with your LED strip.
Never charge or discharge a LiPo outside its recommended voltage range, and use a balance charger designed for your battery’s cell count. Store LiPos in fire-resistant pouches or metal containers if possible. Avoid piercing or bending the cells, and keep them away from extreme heat. If the battery swells or feels abnormally hot, discontinue use immediately. Always match your converter’s input current and voltage ratings to avoid undue stress on the pack.

LiPo batteries excel in portability and power output, but they’re notorious for potential volatility if misused. Because each cell can be damaged by overcharging (above 4.2V) or over-discharging (below about 3.0V), you’ll need specific equipment and vigilance.
Charging Do’s and Don’ts
- Use a LiPo-Compatible Charger: Generic “wall warts” are unsafe for LiPos. Look for balance chargers that ensure each cell within the pack remains at the correct voltage.
- Never Exceed Recommended Charge Rate: Typically 1C for safe, standard charging. So a 2,200mAh pack at 1C means 2.2A charging. Some batteries allow 2C or more, but check the label.
Temperature Monitoring
LiPos can swell or vent if overheated or overcharged. Monitor battery temps, especially during initial charging cycles or if pushing the battery near its discharge limits. A slight warmth is normal; real heat indicates stress.
Physical Protection
If your LED project is mobile (like a costume or portable decoration), ensure the LiPo is well-padded and not at risk of puncture or crushing. A protective case can shield it from accidental impacts.
Disposal
When LiPos degrade, or you suspect damage, discharge them to a safe level (e.g., storage voltage around 3.8V/cell6) and follow local e-waste guidelines7. Never toss them in regular trash without neutralizing the cells.
These steps aren’t meant to deter you from using LiPos but highlight their unique requirements. By paying attention to voltage limits, temperature, and safe charging/discharging methods, you’ll harness LiPo’s benefits for your LED strip while minimizing hazards.
Are There Best Practices for Prolonging Battery Life?
A well-cared-for LiPo battery can power your LED strip for many cycles. Let’s see how to maximize its lifespan.
Avoid deep discharges by not letting voltage dip below ~3.0V per cell, and don’t leave the battery at full charge for extended periods if you’re not using it. Aim for a “storage voltage” around 3.8V per cell if you’ll store it for more than a week. Keeping charge/discharge rates moderate, around 1C or 2C, helps reduce wear, and storing LiPos in a cool, dry place further preserves capacity.
LiPo chemistry thrives on gentle handling. Aggressive usage—like discharging at max current or storing at high temperatures—shortens the battery’s total cycle count (the number of times it can be charged and discharged effectively).
Storage Voltage & Conditions
When you know you won’t use the LED strip for a week or more, setting your LiPo to about 3.8–3.85V per cell is ideal. This is neither fully charged (4.2V) nor fully discharged (~3.0V). Storing at either extreme for long periods stresses the chemical balance. Additionally, keep the battery away from direct sunlight or high humidity—around 10–25°C is comfortable.
Discharge Depth
While LiPos can technically go down to ~3.0V per cell, stopping around 3.2–3.3V extends their life. Some hobbyists set alarms at 3.5V to be extra cautious. The difference might be a little lost runtime, but it spares your cells from damaging low-voltage stress.
Charge Rates
Charging at 1C is typically the safest default. If the pack is 2,200mAh, that means 2.2A. Faster charging (like 2C or 3C) is possible if the battery is rated for it, but repeatedly using high currents can degrade cells faster. For longevity, slower charges are kinder on the chemistry.
Cycle Awareness
LiPos degrade with each charge-discharge cycle, so if you’re running LED strips daily, watch for symptoms like reduced capacity or voltage sag under load. If you see these signs, consider rotating multiple batteries or upgrading to a higher capacity pack.
Following these best practices—avoiding extreme discharge, maintaining safe storage voltages8, and managing charge rates—ensures your LiPo can reliably power your LED strip project for as many cycles as possible.
Conclusion
Yes, you can power an LED strip with a LiPo battery—just match voltage (often via a boost or buck converter), confirm enough current capacity, and handle LiPo safety properly. With the right setup, you’ll enjoy bright, portable lighting without tethering to a wall outlet.
-
Understanding the configuration of three cells in series is crucial for achieving the desired voltage for LED strips, ensuring optimal performance and longevity. ↩
-
A buck-boost regulator is essential for maintaining uniform brightness in LED strips by stabilizing voltage, which is vital for consistent lighting and energy efficiency. ↩
-
A low-voltage alarm is critical for preventing over-discharge of LiPo batteries, safeguarding against reduced lifespan and potential safety hazards. ↩
-
Learning about LiPo balancing is essential for safely combining multiple LiPo packs, ensuring longevity and safety of your battery setup. ↩
-
Exploring the impact of buck/boost converters on battery current draw is crucial for designing efficient power systems, preventing overheating and underpowering. ↩
-
Properly discharging LiPo batteries to storage voltage is essential for safety and battery health. ↩
-
Following local e-waste guidelines ensures environmentally responsible disposal of LiPo batteries. ↩
-
Knowing the safe storage voltages for LiPo batteries is crucial for preventing damage and extending their lifespan, keeping your LED projects running smoothly. ↩